We have 2 papers accepted by AAAI 2026!
We have two papers accepted by AAAI 2026 ! One oral paper contributes to the field of continual learning, addressing the storage burden and data privacy concerns in exemplar-free continual video action recognition. The other paper focuses on large model merging, solving the problem of reasoning capability degradation when integrating long chain-of-thought models with domain-specific models. Detailed information about each publication is provided below.
Paper 1: Rep Deep & Machine Learning: Exemplar-Free Continual Video Action Recognition via Slow-Fast Collaborative Learning
Authors: Xueyi Zhang, Chengwei Zhang, Zheng Li, Xiyu Wang, Siqi Cai, Mingrui Lao, Yanming Guo,Huiping Zhuang
Abstract:
In real-world applications, video action recognition models must continuously learn new action categories while retaining previously acquired knowledge. However, most existing approaches rely on storing historical data for replay,which introduces storage burdens and raises data privacy concerns. To address these challenges, we investigate the problem of Exemplar-Free Continual Video Action Recognition (EF-CVAR) and propose a novel framework named Slow-Fast Collaborative Learning (SFCL). SFCL integrates two complementary learning paradigms: a slow branch based on gradient-driven deep learning, which provides strong adaptability to new tasks, and a fast branch based on analytic learning (e.g., Recursive Least Squares), which efficiently preserves old knowledge without requiring access to past samples. To enable effective collaboration between the two branches, we design the Slow-Fast Dynamic Reparameterization (SFDR) mechanism for adaptive fusion, and the Knowledge Reflection Mechanism (KRM), which mitigates forgetting and task-recency bias via pseudo-feature generation and dual-level knowledge distillation. Extensive experiments on UCF101, HMDB51, and Something-Something V2 demonstrate that SFCL achieves superior performance compared to existing replay-based methods, despite being exemplar-free. Notably, in long-duration continual learning scenarios, SFCL exhibits remarkable robustness, achieving up to a 30.39% improvement in accuracy over baselines while maintaining a low forgetting rate, highlighting its scalability and effectiveness in real-world video recognition tasks.
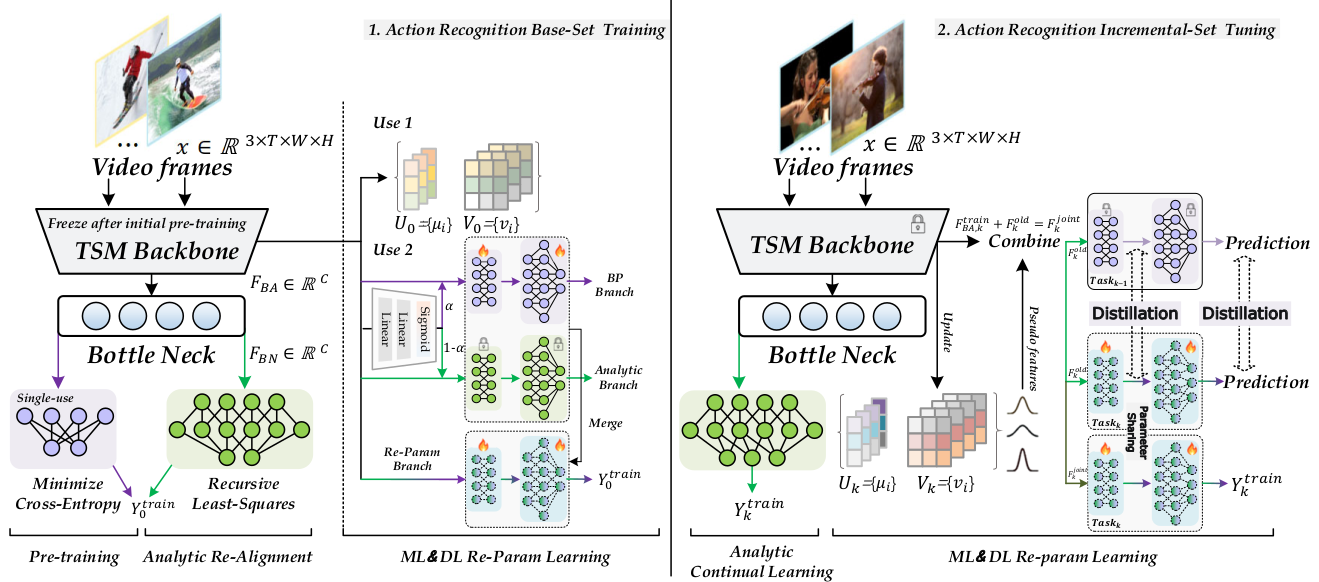
Overall structure of the proposed method
Paper: [To be added]
Code: [To be added]
Paper 2: RCP-Merging: Merging Long Chain-of-Thought Models with Domain-Specific Models by Considering Reasoning Capability as Prior
Authors: Junyao Yang, Jianwei Wang, Huiping Zhuang, Cen Chen, Zigian Zeng
Abstract:
Large Language Models (LLMs) with long chain of thought (CoT) capability, termed Reasoning Models, demonstrate superior intricate problem-solving abilities through multi-step long CoT reasoning. To create a dual capability model with long CoT capability and domain specific knowledge without substantial computational and data costs, model merging emerges as a highly resource efficient method. However, significant challenges lie in merging domain specific LLMs with long CoT ones since nowadays merging methods suffer from reasoning capability degradation, even gibberish output and output collapse. To overcome this, we introduce RCP Merging: Merging Long Chain of Thought Models with Domain Specific Models by Considering Reasoning Capability as Prior, a novel merging framework designed to integrate domain specific LLMs with long CoT capability, meanwhile maintaining model performance in the original domain. Treating reasoning model weights as foundational prior, our method utilizes a reasoning capability indicator to preserve core long CoT capability model weights while selectively merging essential domain specific weights. We conducted extensive experiments on Qwen2.5 7B, Llama3.1 8B, and Qwen2.5 1.5B models in BioMedicine and Finance domains. Our results show that RCP Merging successfully merges a reasoning model with domain specific ones, improving domain task performance by 9.5% and 9.2% over state of the art methods, without significantly harming the original long CoT reasoning capability.
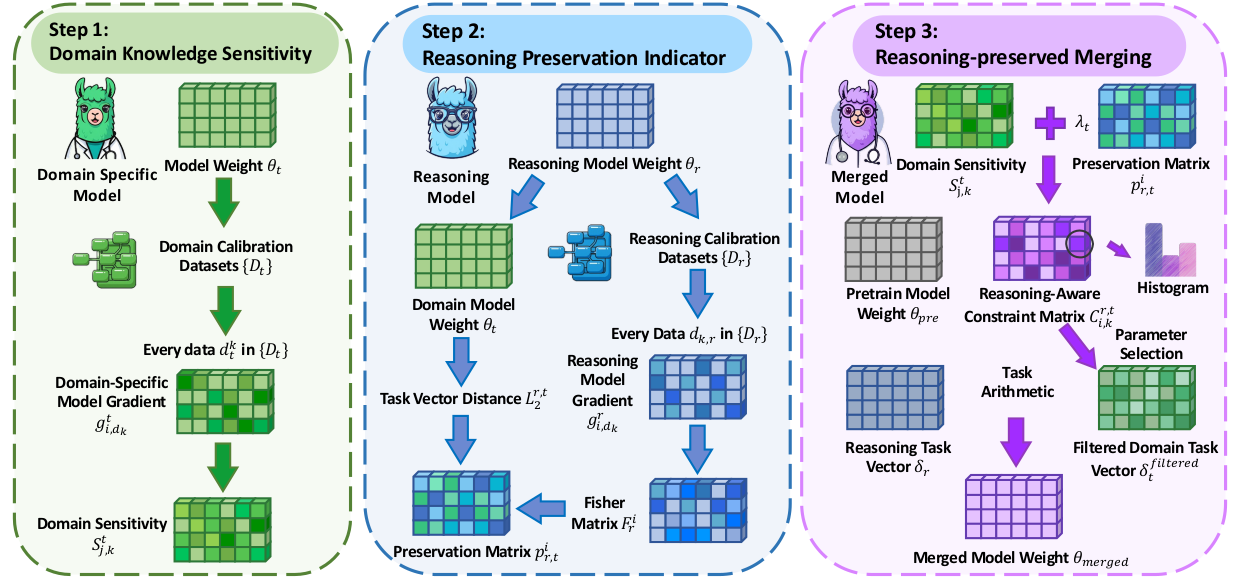
RCP-Merging consists of three stages
Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.03140